In a recent paper published in Cancer Cell, researchers have identified patterns of immune cells within tumours that help with predicting if patients with renal/kidney cancer will respond to successfully to immunotherapy (Figure 1 represents the graphical abstract).
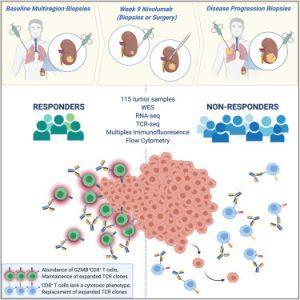
Figure 1: ADAPTeR is a phase II study of nivolumab (anti-PD-1) in treatment-naive patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Through multi-omic analysis of multiregion tumor biopsies taken pre and post-treatment, Au et al. evaluate genomic and tumor immune microenvironment features underpinning anti-PD-1 response and resistance using bulk and single-cell approaches (Au, et al., 2021).
The most common type of kidney cancer, comprising 75% of cases, is clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Treatment of this form of cancer usually involves immunotherapy which is a form of drug treatment guiding immune cells into recognising and attacking cancer cells. However, this is not always effective and may not be successful, particularly for kidney cancers as there is no way to currently predict if it will be effective in an individual patient.
Au, et al., investigated 115 tumour samples from 15 people suffering from metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma, all of whom were receiving immunotherapy drug nivolumab as part of the ADAPTeR clinical trial. ADAPTeR is a prospective, phase II study of nivolumab (anti-PD-1) in 15 treatment-naive patients (115 multiregion tumor samples) with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) aiming to understand the mechanism underpinning therapeutic response. In this study the authors presented an integrated analysis of response to nivolumab and whole-exome and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), TCR profiling, and immunohistochemistry/multiple immunofluorescence (IHC/mIF); as well as high-dimensional flow cytometry across longitudinal, multiregion fresh tumor samples in this cohort (Figure 2). It was imperative for this study that multiple samples were taken from different parts of the kidney tumours as well as tumours that have spread to other organs as from each patient as this provided them with a comprehensive analysis of the effects of the drug and for metastatic profiling.
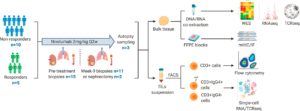
Figure 2: Experimental workflow. Overview of experimental workflow. The numbers (n) of patients contributing to sample collection at different timepoints are shown.
The study focused on harvesting tumour samples at various stages of cancer treatment i.e. before immunotherapy, nine weeks after treatment started, after surgery (at tumour removal), and if the treatment seized and stopped working. It must be noted that for three individuals, samples were collected after the patient had died (PEACE post-mortem research programme).
Au, et a., reviewed aimed to charactise the different tumours and measure the immune response to see any positive response to immunotherapy. They reported through genomic analyses show no correlation between tumour molecular features and response, whereas ccRCC-specific human endogenous retrovirus expression indirectly correlates with clinical response. In addition, the T cell receptor (TCR) analysis revealed a significantly higher number of expanded TCR clone’s pre-treatment in responders suggesting pre-existing immunity (Figure 3). Maintenance of highly similar clusters of TCRs post-treatment predict response, suggesting ongoing antigen engagement and survival of families of T cells likely recognizing the same antigens. In responders, nivolumab-bound CD8+ T cells are expanded and express GZMK/B. In short, they found that the increased number of specific T cell receptors (clones), proteins present in the tumour before treatment, correlated with an increased chance of positive immunotherapy response. In addition, if the T cell receptors numbers were maintained during treatment, this was a sufficient predictor that treatment would be effective. This is an important study as it elucidates why immunotherapy sometimes works and sometimes doesn’t.
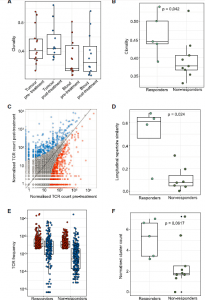
Figure 3: TCR-seq demonstrates maintained clonal expansion through persistent antigenic stimulation associate with nivolumab response. (A) The intratumoral and peripheral TCR repertoireclonality scores are shown for each patient at each time point. (B) The intratumoral TCR repertoire clonality scores pre-treatment are shown for each patient, categorized by response to nivolumab. Mixed-effect model p value shown. (C) Correlated clone sizes in tumor samples. Scatterplots of tumor clone size pre- and post-treatment are shown for all patients. Clones are colored by expansion/contraction status (STAR Methods). (D) The intratumoral similarity (cosine) scores between pre-treatment (red) and on-treatment (blue) are shown for each patient (n = 12). Patients are split between responders and non-responders. Responding patients exhibit greater cosine score, with the two-sided Mann-Whitney test p value shown. (E) The frequency distribution of the intratumoral expanded TCRs pre-treatment (red circles; n = 469 individual TCRs combined from 12 patients) and post treatment (blue circles). Only TCRs that were detected post-treatment were included. (F) The clustering algorithm was run on all patients, and the pre-treatment normalized number of clusters for the networks containing expanded sequences is shown. Two-sided Mann-Whitney test p value shown; n = 14 patients. The minimum and maximum are indicated by the extreme points of the box plot; the median is indicated by the thick
horizontal line; and the first and third quartiles are indicated by box edges.
In their own words:
“In conclusion, in this prospective study, we reveal features of anti-PD-1 response and resistance in ccRCC. We identified tumor-specific T cells with cytotoxic features in ccRCC, which hold promise for development of adoptive cellular therapy for this cancer…this dissection of immune changes under nivolumab provides the foundation for understanding response to combination therapies. Finally, our multi-omic analysis framework provides a template and highlights challenges for future immuno-oncology biomarker studies in ccRCC.” (Au, et al., 2021).
Journal Article: Au, et al., 2021. Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell.
Summary by Stefan Botha










