A new study describes the development of a high-throughput, quantitative immunoassay that can identify and differentiate immune responses from Mpox infection versus Orthopoxvirus vaccination. This innovation could improve Mpox surveillance and vaccine monitoring globally.
Key Findings
The multiplex immunoassay detects IgG antibodies to three key Mpox and Orthopoxvirus proteins:
- A29: a highly specific Mpox marker
- A35 & B6: shared by Mpox and vaccinia-based vaccines (e.g., JYNNEOS, ACAM2000)
The assay was tested using human serum samples from:
- Mpox-infected individuals
- Vaccine recipients (JYNNEOS, ACAM2000)
- Orthopoxvirus-naive controls
Results showed distinct antibody profiles:
- Mpox infection → Strong response to A29, A35, and B6
- JYNNEOS/ACAM2000 vaccination → Strong response to A35, B6, but minimal or no A29.
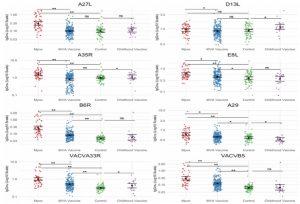
Figure 1: Significantly different IgG titres across groups. Each graph represents the IgG titres for that antigen for each group. Mpox (n = 54), MVA Vaccine (n = 229), Control (n = 78), Childhood Vaccine (n = 22). The error bars represent the geometric mean titre (GMT) and the 95% confidence interval of the GMT for each group. Each antigen in this figure had significantly different titres across the four groups by Kruskal–Wallis Test (all p < 0.05). Comparisons shown represent p values as per post-hoc Dunn’s test to assess differences in titres between Mpox, MVA Vaccine, Control and Childhood Vaccine group with *p = 0.0001–0.05, **p < 0.0001, and ns = not significant.
The assay is quantitative and scalable, enabling:
- Seroprevalence surveys
- Monitoring vaccine-induced immunity
- Differentiation of natural infection from vaccination.
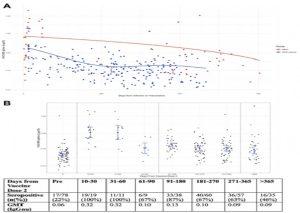
Figure 2: Antibody responses over time. A: VACV BS lgG Responses over time post MVA-Vaccination and Mpox Infection. A: Change in VACVB5 IgGnu titres over time since onset of symptoms of Mpox or dose 2 of MVA vaccination. We modelled change in VACVB5 IgGnu over time using scatter plots with superimposed curves fitted using generalised additive mixed models (GAMM), with a Gaussian link function and time since symptom onset or vaccination fitted as a spline. B: VACV BS IgG Responses over time post MVA-Vaccination. B: VACVB5 IgGnu titres over time before and after MVA vaccination. The centre of the error bar represents the geometric mean titre with the error bars representing the 95% confidence interval of the GMT. Seropositive is defined as the threshold identified by the Youden Index with the optimum sensitivity and specificity (0.082 IgGnu) from the ROC curve analysis for VACVB5 IgG.
Public Health Impact
This tool supports Mpox control efforts by allowing:
- Better assessment of population immunity
- Identification of breakthrough infections
- Improved guidance for vaccination strategies
Further work is needed to:
- Validate the assay in diverse global settings
- Adapt it for point-of-care use
- Expand it for other Orthopoxviruses (e.g., smallpox, cowpox)
Journal article: Parrino, J., et al. 2024. Development and validation of a quantitative Orthopoxvirus immunoassay to evaluate and differentiate serological responses to Mpox infection and vaccination. PLOS ONE.
Summary by Ezediuno Louis Odinakaose










