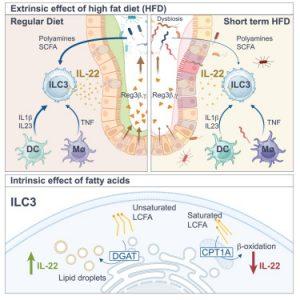
New research reveals that even short-term exposure to a high-fat diet can immediately impair gut immunity—long before any physical symptoms appear (Figure 1). The study offers the first direct evidence of how quickly saturated fats can weaken the gut’s natural defences, laying the groundwork for chronic inflammatory diseases.
The study found that just two days of consuming foods high in saturated fat was enough to reduce levels of interleukin-22 (IL-22) – a protein crucial for maintaining gut health and controlling inflammation. The underlying origins of inflammation associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), coeliac disease, and rheumatoid arthritis have remained elusive.
Mice in the study appeared outwardly healthy despite a measurable decline in gut function after just a few high-fat meals. There were no visible signs of inflammation, such as weight gain or discomfort, but immune profiling revealed early disruption of protective mechanisms in the gut lining.
At the centre of the findings is IL-22, a key immune protein that supports the gut lining and helps prevent inflammation. High-fat diets deal a blow to gut health: they not only promote inflammation but also suppress the body’s ability to protect itself.
Interestingly, the study also found that unsaturated fats – like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil – had the opposite effect, increasing IL-22 levels and enhancing gut resilience. The researchers believe this pattern would likely hold true in humans as well.
The team was able to restore gut health in mice by replenishing IL-22 levels, suggesting that targeted therapies could one day help prevent or treat gut inflammation. But their focus, for now, is on natural, diet-based approaches. The findings highlight the potential for dietary guidelines to be refined based on molecular insights – promoting unsaturated fats not just for heart health, but for immune health as well.
As the connection between diet and immune function becomes clearer, this study marks a critical step toward preventative nutrition strategies that address inflammation at its root – before it has a chance to take hold.
Journal article: Xiong, L., et al. 2025. Acute exposure to high-fat diet impairs ILC3 functions and gut homeostasis. Immunity.
Summary by Stefan Botha